- Windows Rights Management Services Client
- Windows 10 Rights Management Services
- Microsoft Rights Management Service
Here are all ways you can use to access the Administrative Tools in Windows 10. RECOMMENDED: Click here to fix Windows errors and optimize system performance. Table of contents. Open Administrative Tools from Start Menu. Open Administrative Tools from Settings. Open Administrative Tools from Control Panel.
Information Security
Any of your audio or video files have Windows Media Digital Rights Management (WMDRM). This includes music files in the WMA format that you ripped from CDs using Windows Media Player (any version up to Windows 10 version 1511) with the “copy protect music” option selected. Aug 06, 2015 I have been using Windows Rights Management for some years to protect some files. Occasionally I am asked to sign in and it works again, however I am now completely unable to access my files. I get a box headed Windows Rights Management, which sometimes stays blank and other times asks if I. Ganttman I can only offer additional info that users. Rights Management Services (RMS) We have not been able to successfully send attachments using RMS and can only view text within an email. We were instructed to download attachments, however nothing happens when you try to download. Microsoft rights management services free download - Microsoft Windows Rights Management Services Client with Service Pack 2 - IA64 Edition, Microsoft Windows Rights Management Services Client. Apr 19, 2017 Windows 10 Provides an overview and links to information about the User Rights Assignment security policy settings user rights that are available in Windows. User rights govern the methods by which a user can log on to a system. User rights are applied at the local device level, and they allow users to perform tasks on a device or in a domain.
Windows Rights Management Services Client
Defending the digital infrastructureWindows Rights Management Services
Microsoft
Price: Starts at $37 per user
@exb
| Microsoft's Windows Rights Management Services |
E-mail and IM can put it in a competitor's hands in a heartbeat; it can walk out the door on a CD, USB stick, MP3 player or laptop hard drive. Regulations like HIPAA and SOX pile civil and criminal penalties on top of traditional business risks.
Much of this critical information is created in ubiquitous Microsoft Office apps--Word, Excel, Outlook, PowerPoint--which is, in itself, a strong case for considering Windows Rights Management Services (RMS) to identify and protect sensitive documents.
For example, a user could apply a rights policy to a Word document that allows members of the accounting department to modify the contents, and denies access to everyone else in the organization. Unlike traditional ACL entries used on all file servers, these permissions are embedded within the document, so that it's protected even if it's sent off site.
With the release of its first Service Pack, Microsoft has significantly improved RMS. It's now FIPS-compliant and supports two-factor authentication and non-Internet connected 'air gap' networks. The management console GUI is improved, as is the software development kit for enabling RMS use with custom applications. We tested a variety of policies for both documents and e-mail, and the product performed flawlessly. We were able to share documents among multiple users with various levels of access, and strictly control whether e-mail could be forwarded to unauthorized users.
RMS does a nice job separating administrative and content rights. For example, if you're an attorney handling highly confidential client matters, you want system administrators to be able to maintain the various systems and data that the organization uses, but not have access to the actual content. This type of situation is very common in highly secure classified military environments.
RMS consists of a Web-based management server and an Microsoft SQL Server back end. Administrators use the management console to define and distribute rights management policies.
Setup and installation of the management console is fairly straightforward--basic services can be up and running in about 30 minutes. No client software is required for Windows 2000/XP.
MS Office 2003 offers the most seamless experience. Office 2000 users can access and manipulate documents using an Internet Explorer plug-in depending on policy, but the integration, look and feel aren't nearly as good.
| Exec Summary | ||||||||
| ||||||||
Although RMS is fairly easy to implement technically, the most significant barrier of deployment is organizational planning, especially if you want to share RMS-protected content with extranet partners. If this is the case, you'll have to carefully identify cross-organizational trust issues: Does each party maintain its own infrastructure, or does it share the other's resources? How does one party let the other know about employee change/add/delete requests?
If you're ready to invest the time upfront, RMS is a good solution to a big problem and will allow your organization to securely collaborate with extranet partners without worrying about whether or not sensitive materials will mysteriously find their way to the Internet.
--PETER GIANNACOPOULOS
Dig Deeper on Data security technology and strategy
Broadcom-Symantec deal troubles cybersecurity experts
What are the pros and cons of outsourcing IT security?
How to become an incident responder: Requirements and more
Conquering cloud security threats with awareness and tools
Broadcom-Symantec deal troubles cybersecurity experts
Forcepoint pushes 'human-centric cybersecurity' approach
New programs released aim to improve Google Cloud security
AWS moves to curb S3 data leaks, but Chris Vickery is doubtful
Conquering cloud security threats with awareness and tools
risk analysis
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language)
Bolster your DLP strategy with help from the cloud and CASBs
What are the pros and cons of outsourcing IT security?
How to become an incident responder: Requirements and more
Zero-trust security means new thinking plus practical steps
Bolster your DLP strategy with help from the cloud and CASBs
Conquering cloud security threats with awareness and tools
Container security best practices help mitigate risks and threats
Government cybersecurity problems can teach enterprises what to do
What's the best way to protect sensitive information while traveling?
Cybersecurity and Applied Mathematics
Behavioral threat assessment means real-time threat detection
Government cybersecurity problems can teach enterprises what to do
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 end of life: When's the time to migrate?
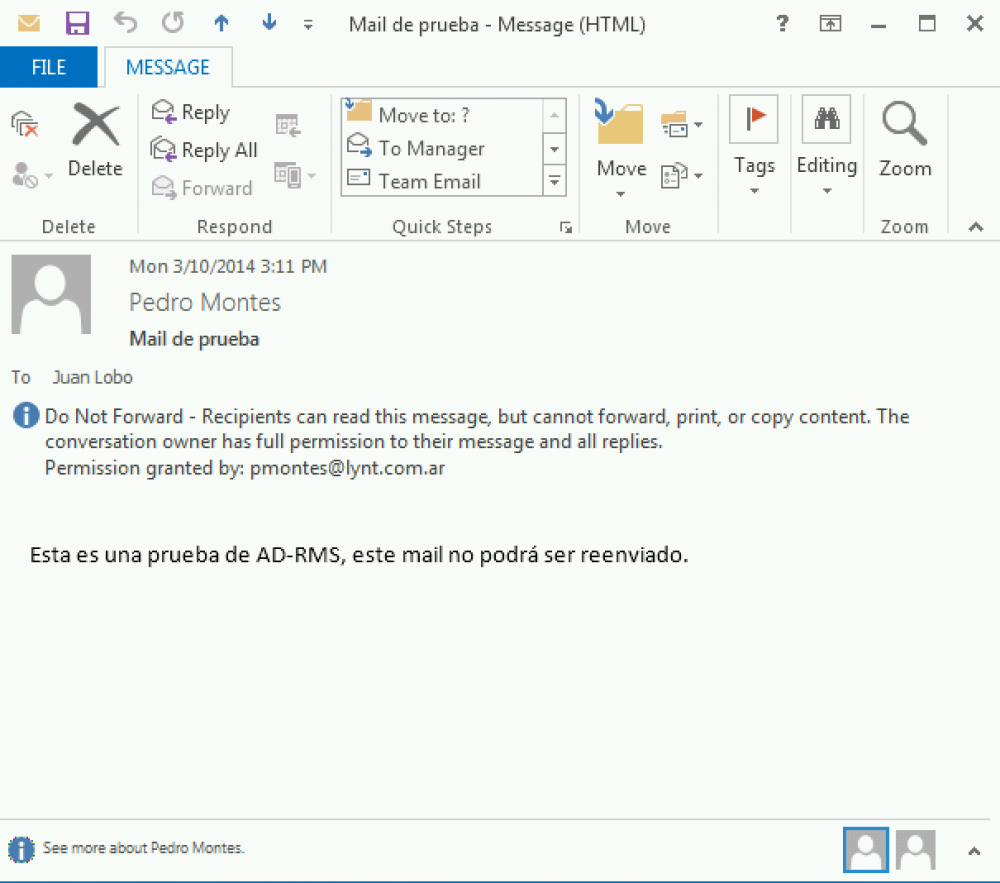
Information Rights Management (IRM) helps prevent sensitive information from being printed, forwarded, or copied by unauthorized people. The permissions are stored in the document, workbook, presentation, or e-mail message, where they are authenticated by an IRM server.
To view rights-managed content that you have permissions to by using Office, just open the document, workbook, or presentation.
The first time that you open a document, workbook, or presentation with restricted permission, you'll connect to a licensing server to verify your credentials and to download a use license.
If you want to view the permissions you have, either click View Permission in the Message Bar or click one of the following in the status bar at the bottom of the screen:
This document contains a permissions policy
This workbook contains a permissions policy
This presentation contains a permissions policy
Open the document that has restricted permissions.
If this is the first time that you are accessing the licensing server, enter your user name and password for the licensing server, and then select the Save password in Mac OS keychain check box.
Tip: If you do not select the Save password in Mac OS keychain check box, you might have to enter your user name and password multiple times.
The Message Bar appears and displays a message that the document is rights-managed. On the Message Bar, click View Permissions.
Note: If you have Full Control permission, the Message Bar displays Change Permissions.
Under Permissions, view the list of tasks that you can perform with the file. Under Restrictions, view the list of tasks that you cannot perform with the file.
Information Rights Management (IRM) helps do the following:
Prevent an authorized recipient of restricted content from forwarding, copying, changing, printing, faxing, or pasting the content for unauthorized use
Restrict content wherever it is sent
Provide file expiration so that content in documents can no longer be viewed after a specified time
Enforce corporate policies that govern the use and dissemination of content within the company
Windows 10 Rights Management Services
IRM can't prevent restricted content from being:
Microsoft Rights Management Service
Erased, stolen, or captured and transmitted by malicious programs such as Trojan horses, keystroke loggers, and certain kinds of spyware
Lost or corrupted because of the actions of computer viruses
Hand-copied or retyped from a display on a recipient's screen
Digitally photographed (when displayed on a screen) by a recipient
Copied by using third-party screen-capture programs